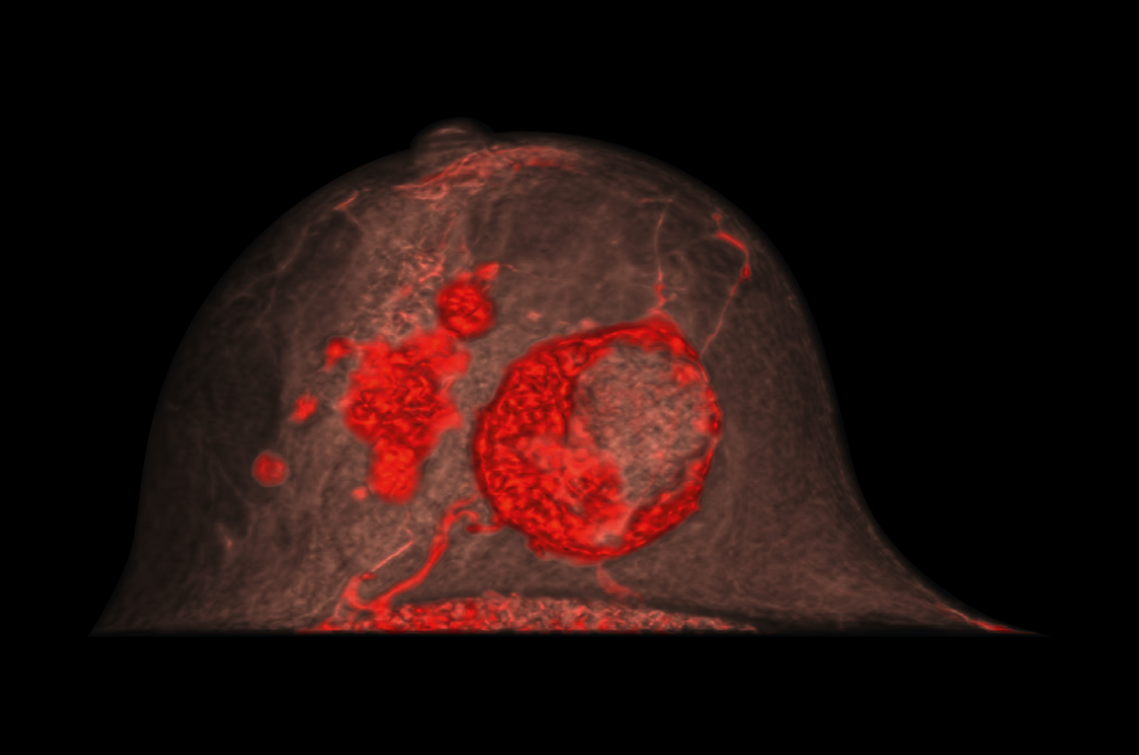
Detection of malignant breast lesions in imaging: comparison of contrast-enhanced spiral breast computed tomography and mammography
Mammography is the most common imaging method for breast cancer screening. However, the two-dimensionality of the procedure significantly limits its sensitivity - especially with a higher breast density. Contrast-enhanced spiral breast computed tomography (breast CT) could overcome this limitation thanks to its three-dimensionality, high resolution and low noise level. In a recent retrospective study, the detection capability of both methods for detecting malignant lesions in the breast was therefore directly compared for the first time. Contrast-enhanced breast CT scored highly thanks to its high detection capacity, which is independent of breast density, and its high diagnostic reliability.
A total of 90 women (59.5 ± 9.5 years) were included in the study by Wetzl et al.1 between October 2019 and February 2022. All women had biopsy-confirmed breast cancer and had been additionally examined by contrast-enhanced or non-contrast-enhanced breast CT after a mammogram (nu:view; AB-CT-Advanced Breast-CT GmbH, Erlangen, Germany). The mammography devices used only allowed 3-D visualization on the basis of sectional images, whereas the nu:view breast CT produces true 3-D images without superimposition. Two certified radiologists independently evaluated the mammography and breast CT data sets and categorized breast density using recognized methods.2, 3 Diagnostic accuracy was assessed on a 4-point scale.
Aims of the study
Comparison of the detection capability of mammography and contrast-enhanced or non-contrast-enhanced breast CT for the detection of malignant breast lesions
Comparison of this detection capability as a function of breast density
Evaluation of histopathologically detected lesions using the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) descriptors3 (focal lesions, microcalcifications, architectural defects, enhancement without focal lesion [Nonmass enhancement])
Results
[1] The detection capability in detecting malignant breast lesions was significantly higher with contrast-enhanced breast CT than with mammography (P ≤ 0.001 for both examiners) and non-contrast-enhanced breast CT (P ≤ 0.001; difference to mammography P = 0.004; Table 1).
[2] The detection capability for malignant breast lesions was almost independent of breast density in contrast-enhanced breast CT (Fig. 1). With mammography and non-contrast-enhanced breast CT, the detection capability decreased significantly with increasing breast density (P ≤ 0.001 for both examiners). The diagnostic reliability of contrast-enhanced breast CT was very high or high in 97.2 % of cases (mammography 81.4 %, non-contrast-enhanced breast CT 74.1 %).
[3] The diagnostic contribution of various BI-RADS descriptors differed between the methods:
- focal lesions contributed 96.2% and 98.6% to the detection of malignant lesions on contrast-enhanced and non-contrast-enhanced breast CT, respectively (mammography: 84.0%)
- Microcalcifications were detected less frequently with contrast-enhanced and non-contrast-enhanced breast CT (14.4 %, 20.3 %) than with mammography (25.5 %). The same applied to architectural abnormalities (contrast-enhanced and non-contrast-enhanced breast CT 4.8%, 8.1%; mammography 28.7%).
- Enhancements without focal lesions (nonmass enhancement) were only detected in contrast-enhanced breast CT (18.3 %).
Conclusion
Contrast-enhanced breast CT has a very high detection capacity and can detect malignant breast cancer lesions regardless of the patient's breast density. In contrast, the detection capability of non-contrast-enhanced breast CT and mammography decreased with increasing breast density. Contrast-enhanced breast CT showed high diagnostic reliability and was also able to visualize non-mass enhancement.
Sources
1Wetzl M, et al. Detectability of Breast Cancer in Dedicated Breast CT Compared With Mammography Dependent on Breast Density. Invest Radiol 2024,59, 861-5.
2Wieler J, et al. Breast density in dedicated breast computed tomography: Proposal of a classification system and interreader reliability. Medicine (Baltimore) 2021,100, e25844.
3D'Orsi CJ SE, Mendelson EB, et al. ACR BI-RADS Atlas, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System; American College of Radiology: Reston, VA, 2013.